SAP HR Employee Data Maintenance
by Faisal Iqbal
 Among the various activities which HR departments perform is Employee Data Maintenance as part of their day-to-day operations. Many companies use SAP as their Enterprise Resource Planning solution, across businesses, and its SAP HCM key module (SAP Human Capital Management - formerly known as SAP HR / SAP Human Resources) to manage core HR and Payroll functions, including training and event management, employee records, and personal information of employees.
Among the various activities which HR departments perform is Employee Data Maintenance as part of their day-to-day operations. Many companies use SAP as their Enterprise Resource Planning solution, across businesses, and its SAP HCM key module (SAP Human Capital Management - formerly known as SAP HR / SAP Human Resources) to manage core HR and Payroll functions, including training and event management, employee records, and personal information of employees.
Creating SAP HR Structures
SAP Time Management, SAP Payroll & Benefits, or Employee data can be best managed by classifying an Organization and its People into different categories. In the SAP human resource management system, such classifications, from an organizational management point of view, are called:
- Enterprise Structure
- Personnel Structure
The first structure allows SAP Customers to classify their organization according to Pay Scales and Work Schedules, which could be based on Locations or Functions of Organizational Units. In SAP, the main elements are the Personnel Area and Personnel subarea.
The second structure is used by companies to classify their employees according to the employment status and agreement. The classification is maintained in the SAP system as Employee Group and Employee subgroup.
Maintaining SAP HR Data
Employee Data is maintained in so-called Information Types, also known as InfoTypes, to group related data fields together. An Infotype may have a subtype too.
The InfoType records can be
- Created when an entry doesn't exist,
- Changed if a record has to be corrected,
- Copied from earlier record to a new one,
- Delimited when the record isn't valid anymore,
- Displayed as Single or Multiple entries, and
- Deleted if the record was created mistakenly.
SAP HR Data can be stored in different ways:
- Master Data Maintenance is used where a single InfoType record has to be maintained for one employee at one time,
- Personnel Action Transaction is used when a procedure has to be carried out on a single employee, requiring maintenance of multiple InfoTypes in some sequence, and
- Fast Entry is used when a single InfoType has to be maintained for Multiple Employees at once, such as payment of a special allowance to a specific group of employees.
The most common InfoTypes include Personal Data, Family/Related Person, Addresses, Bank Details, Organizational Assignment, Planned Working Time, Payroll Status, Basic Pay, Recurring Payments/Deductions, Additional Payments, Loans.
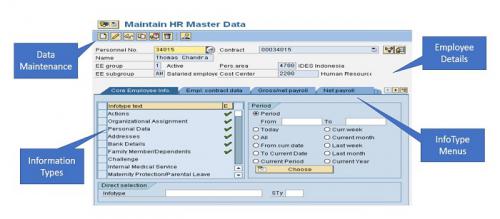
Image: Maintain HR Master Data – IDES
SAP HR Configuration
Personnel Administration component can be customized to a great extent, including the following:
- InfoType Specific Settings: The standard SAP system provides some default values and settings, which can be changed. For instance, the Personal Data InfoType includes a form of address, such as Mr., Ms., Mrs., etc. If required, you can modify the list of options.
- InfoType Menus: To control who can maintain specific types of data, you can limit the list of InfoTypes in a menu to specific SAP users. This is done by creating User Groups and assigning them to an employee's user record; for example, HR Administrators in different countries can be assigned to different User Groups.
- Actions: Certain types of Employee Data are maintained in a particular sequence when specific procedures are followed. The system behavior, as to which record to display, and for which User Group, can be controlled through Info Group settings. Hiring an employee, for example, requires maintenance of multiple records – different InfoTypes.
- Dynamic Actions: Some of the data maintenance can be based on meeting certain conditions. For instance, if you are maintaining one InfoType record and want to maintain another at the same time, you can define the link between the two using Dynamic Actions. For example, if a person's marital status is changed in Personal Data, the other InfoType (Family/Related Person with Subtype Spouse) also pops up.
- Features: In some cases, default values can be proposed by the system when a specific criterion is fulfilled. By creating a decision tree called 'Feature' in SAP, such behavior could be controlled. For instance, the default Payroll Area for a specific Enterprise or Personnel Structure is automatically populated in the system when the combination of Personnel Areas/Subareas or Employee Groups/Subgroups is entered.
In addition to the above, you can also integrate the Solution with third-party systems.
SAP HR Reporting
The SAP HCM module provides several reporting options to
- View commonly required Employees Details, using Standard Reports,
- Audit Changes made in Employee Data with Date and Time stamp with the User, and
- Create Ad Hoc Reports to query data with custom criteria.
You can learn more about this subject by subscribing to this SAP HR – Personnel Administration course.
by Faisal Iqbal
More Blogs by Faisal Iqbal

Performance and Goals Management with SAP...
Employers want the best from their employees, and employees want their...
Related Blogs

10 Tips for Completing SAP Work Orders
SAP Work Orders are an integral part of the SAP Work Manageme...

The 8 Basic Functionalities of SAP Ariba
Acquired by SAP in 2012 for $4.3 billion, the SAP Ariba netw...

Why Doesn't My ABAP SQL Query Work?
I imagine virtually every ABAP programmer makes common use of the FOR ALL...
.png)

