SAP Preventive Maintenance for Proactive Machine Check-ups
by Ashikul Alam
 SAP Plant Maintenance supports different kind of maintenance activities like; Breakdown maintenance, Shutdown Maintenance, Condition Based Maintenance, and so on.
SAP Plant Maintenance supports different kind of maintenance activities like; Breakdown maintenance, Shutdown Maintenance, Condition Based Maintenance, and so on.
From the word Preventive, we can relate to what preventive maintenance refers to. Yes, exactly what you’re thinking, preventive maintenance helps us to manage our equipment and machineries proactively to prevent incidents and accidents. Preventive maintenance set up generates maintenance tasks for specific equipment based on predefined parameters. So, the overall planning for equipment maintenance is triggered by the system automatically according to the parameters. Eventually, the equipment owner can maintain the equipment effectively by a system that is driven maintenance notification or order.
Preventive maintenance can be categorized into two types:
- Time-Based Preventive Maintenance
- Performance-Based Preventive Maintenance
Time-Based Preventive Maintenance
In time-based maintenance, the system checks the defined time interval to generate the maintenance activities. Based on the total period and time interval maintenance plans are generated.
Performance-Based Preventive Maintenance
The overall master data for time-based preventive maintenance and performance-based preventive maintenance is the same, the only change is in the regular measurement of equipment. Measurements are captured in performance-based maintenance, once the measurements go beyond the defined limits system triggers maintenance requirement. Measurement data can be captured manually or automatically in SAP.
Preventive Maintenance Master Data
1. Maintenance Strategies
In a maintenance strategy, it is been defined how the maintenance plan will be applied for the equipment or machine. I might apply a strategy for every month for specific equipment. Also, some equipment might require maintenance every 4 months or so on. T-code used for maintenance strategy creation is IP11.
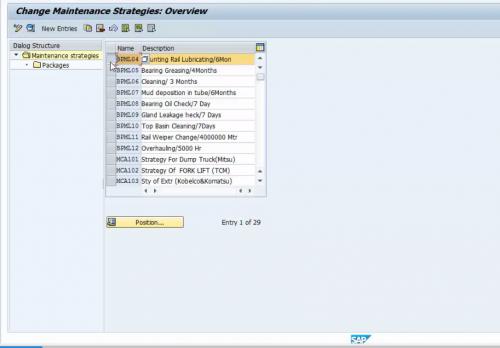
Figure 1 Maintenance Strategy of Different Intervals
In the maintenance strategy, we need to create all the required strategy that is applicable for different equipment. So that the required strategy can be used for relevant equipment.
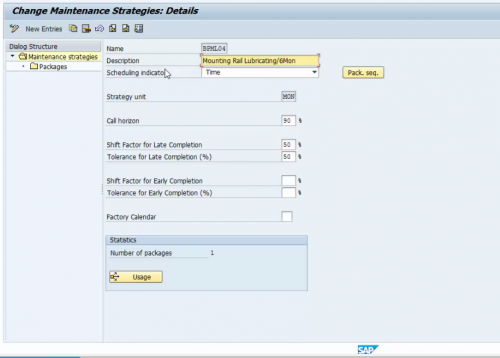
Figure 2 Different Parameters of Maintenance Strategy
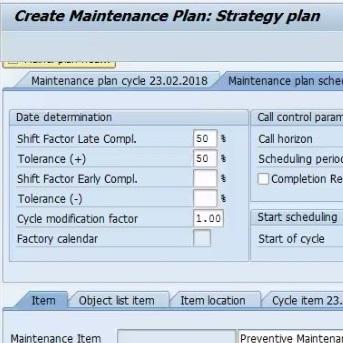
In the maintenance strategy, we maintain the strategy unit whether the strategy is for a day, month, or year. Some key indicators like call horizon, shift factors are maintained as per the business requirement. For example, if we need to have a strategy of 10 days and we set a call horizon 90% then the system will generate a maintenance schedule on the 9th day. So, we’ll get one day to be prepared with relevant man-power and spares. In case, spares purchase has a long lead time we can set scheduling dates even earlier so that spares purchase can be completed before we start the maintenance.
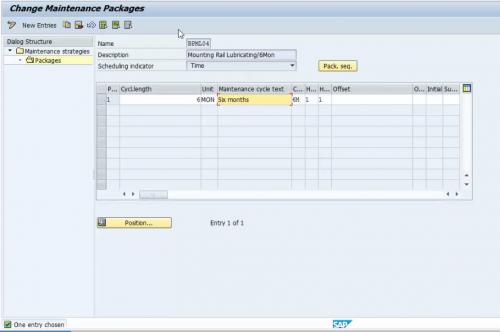
Figure 3 Maintenance Strategy for 6 Months
2. Task List
The Task List is the master data regarding the maintenance task that will be performed for equipment. Step by step operations requirements is listed along with the required hours of man-power. Also, if we required any spare parts for maintenance that is also assigned for operations. Required T-code for task list creation is IA05.
A task list can be equipment specific, or it can be a general task list as well. We defined the plant maintenance category of a task list in the usage filed in the task list.
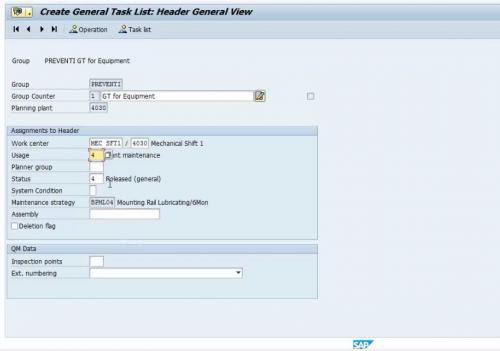
Figure 4 Task Creation with Required Parameters
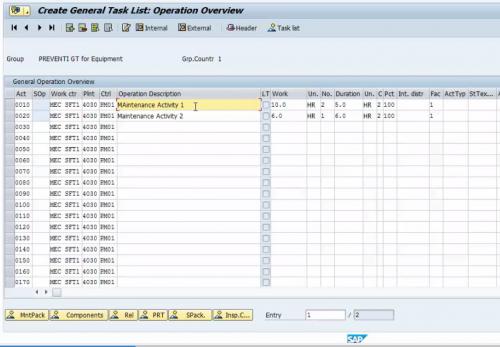
Figure 5 List of Operations and Duration in Task List
3. Maintenance Plan
Now with the created strategy and task list, we need to maintain the plan for the required equipment. A maintenance plan can be maintained for generating maintenance notification or direct maintenance orders. As per business requirements, some company wants maintenance order to be generated directly from maintenance plan, on the other hand, some company wants to keep the control on the maintenance planner whether to generate maintenance order from notification or not. In this below example, we maintained the maintenance plan category as ‘Maintenance Order’, so the order will be generated directly. IP41 is the T-code to create a maintenance plan.
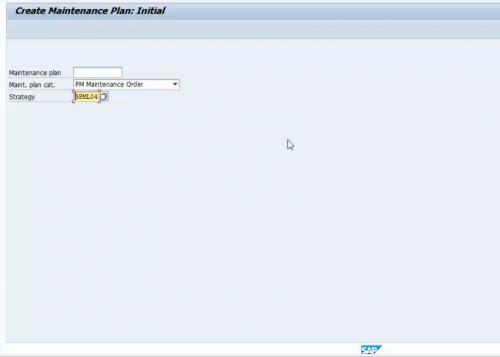
Figure 6 Maintenance Plan Creation with Created Strategy
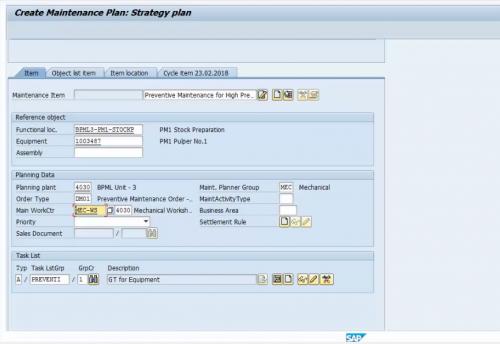
Figure 7 Equipment and Task List Assignment in Maintenance Plan​
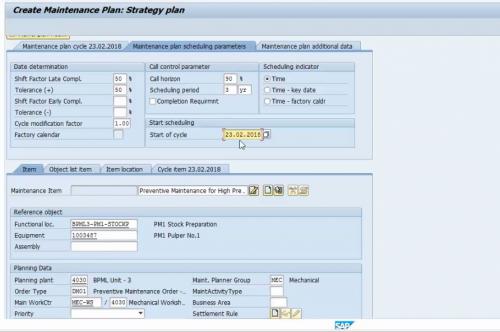
Figure 8 Total Scheduling Period and Start of Cycle Set-up in Maintenance Plan
In the maintenance plan, we defined the total scheduling period for this specific plan. For example, in this maintenance plan, we’re scheduling a plan for a total of 3 years with 6 months interval. Also, we defined the start date from when the cycle will start for all these parameters.
Figure 9 Save Maintenance Plan with All Inputs
After maintaining all the required fields we’ll save the maintenance plan.
Maintenance Order Scheduling
1. Scheduled Maintenance Plan
After creating the plan we need to schedule the plan so that according to the scheduling date maintenance order gets generated. After creating the maintenance plan we need to schedule it for the very first transaction only. Later on, deadline monitoring performs this via a batch job. The maintenance plan schedule T-code is IP10.
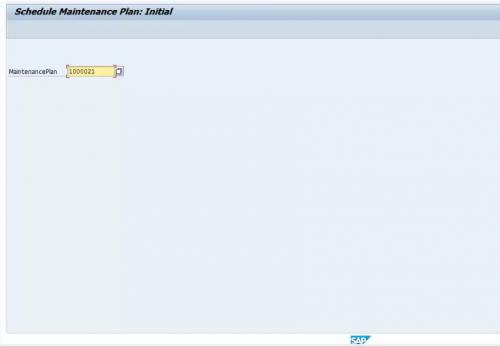
Figure 10 Maintenance Plan Scheduling
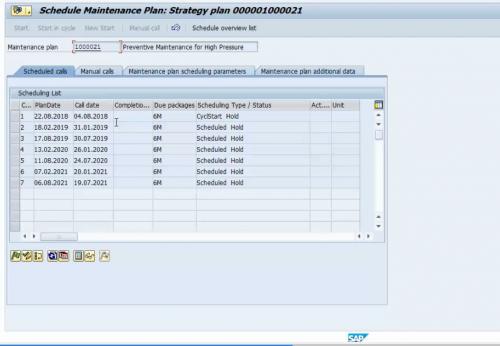
Fig 11 Maintenance Plan with Call Date (related to call horizon) and Plan Date​
As we can see, there are two dates in the scheduled maintenance plan. One is the call date, the other is the planning date. The call date is before the planning date, as per the call horizon that we maintained in the maintenance strategy.
2. Monitor Deadline
This is scheduled maintenance plans that we performed in the previous step. The only difference is, the system will monitor the deadline on its own once we set up this batch job. The batch job might run daily or for a specific interval. If this is for an interval, all the maintenance plan that has scheduling date in that interval will generate maintenance order via the batch job. Deadline monitoring T-code is IP30.
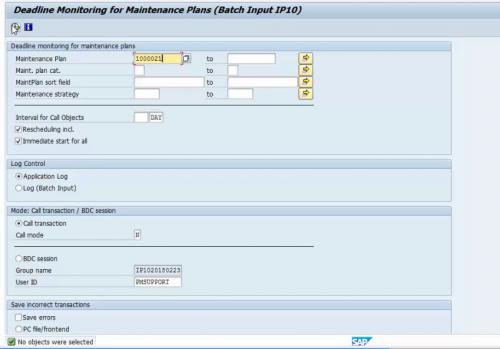
Figure 12 Automatic Deadline Monitoring of Maintenance Plan 1
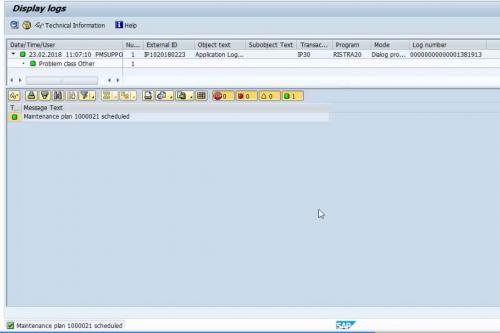
Figure 13 Automatic Deadline Monitoring of Maintenance Plan 2
3. Maintenance Order from Maintenance Plan
Now as we release the first maintenance item, the maintenance schedule has generated the first maintenance order on the required date. However, other maintenance items didn’t generate any order, as the planning date is in the future. Those maintenance items will be counted on a future deadline monitoring transactions as per the timeline. Maintenance Order against a plan can be found from T-code IP24.

Figure 14 Maintenance Order Generation from Deadline Monitoring
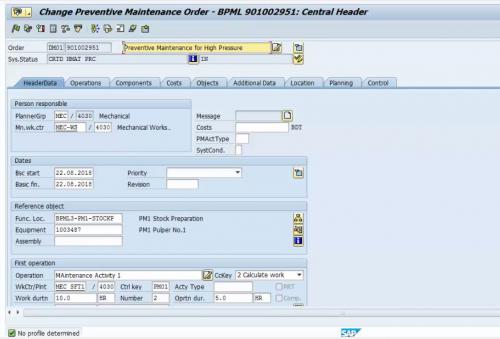
Figure 15 Maintenance Order Details Copied from Master Data of Maintenance Plan
We can see the details of the maintenance order entering the order. The equipment, operations, and required spares all are get copied from the master data that we set in previous steps.
The overall flow for time-based and performance-based preventive maintenance is the same, the only difference is, in performance-based preventive maintenance we measure the maintenance point for equipment. Maintenance notification gets generated when the measurements go beyond the higher or lower limit.
For any SAP Plant Maintenance (PM) module implementation, Preventive Maintenance plays a key role as business gets this benefit of maintaining equipment proactively from system generated maintenance requirements.
by Ashikul Alam
More Blogs by Ashikul Alam
SAP Serial Number Functionality and Configuration
The first feature that comes to mind while writing about the serial nu...

SAP Batch Management Functionality and Configuration
My Batch number was ‘07C’ when I was in college. There wer...

Related Blogs
SAP FIORI Introduction and Architecture
SAP FIORI is the new user experience (UX) and design language for SAP ...

Learn SAP ABAP Tips & Tricks
With vast experience in SAP ABAP (Advanced Business Application Progra...

RESTful ABAP Programming Model (RAP)
Introduction The programming language for SAP, ABAP (Advanced Business...
.png)

