Evolution of Sales Systems: Understanding the Order to Cash process in S/4HANA
by Pramod Bangalore
 The end goal of any organization is to maximize the selling of their products to customers. Effective selling involves an end-to-end supply chain system of procurement, manufacturing and distribution.
The end goal of any organization is to maximize the selling of their products to customers. Effective selling involves an end-to-end supply chain system of procurement, manufacturing and distribution.
Before a sales order is booked in SAP, there are multiple background activities such as: inquiries from customers, quotes and other related activities. Once the sales department agree to sell the product to the buyer, a sales order is then created in an ERP.
Over a period, the selling process of reaching the end consumer has evolved, and at the same time, information technologies have empowered business in executing the end-to-end process with control and visibility.
Speaking of Sales...download our newest SAP cheat sheet here:
SAP Sales & Distribution Cheat Sheet
Redefining how business is done
Digitization has been a big game changer in recent years by redefining how business is done. Both the selling process and reaching out to the end customer has been redefined. Conventionally, the sales process was managed in an internal ERP system of an enterprise. However, functions like lead generation, visibility to sales pipeline and promotion activities are not part of an ERP function.
Therefore, to capture and analyze customer needs and preferences, customer relationship management (CRM) concept and IT systems were designed and developed. The SAP CRM system helps in streamlining presales and sales function before the actual sales order is created in an ERP system.
In a sale, there are a number of channels like wholesale, stockiest and retail before it actually reaches the end consumer. OEM’s (original equiptment manufacturers) generally lose the visibility once it sells to the first channel in the hierarchy. This is why dealer management systems came into existence. Dealer management systems capture the channel sales after the goods move out of the OEM’s warehouse.
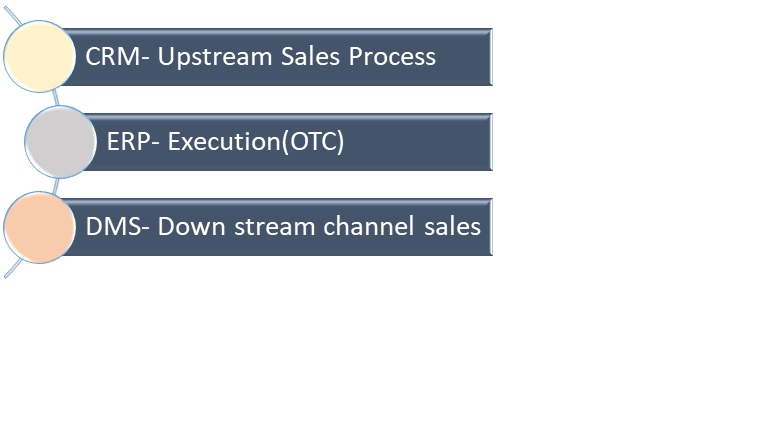
The present digitization era landscape of sales systems has evolved as below:
CRM, ERP & DMS
ERP was THE front-end system in late 1990’s an early 2000's. End-to-end transactions were captured in an ERP and there was no visibility in a system of the activities before the sales orders were booked. Customer relation management system (CRM) came into existence to enable and maintain the relationship with the customer in a systematic manner and capture their needs and preferences. CRM quickly gained momentum and expanded the scope into sales force management, sales pipeline management and after sales, which a conventional ERP was not designed to handle.
“CRM evolved as the front-end system and ERP became the backend execution system”.
CRM and ERP had data in silo, enterprises linked both the systems to leverage data from both the systems which empowered them to service the customers better and increase the order hit rate with customers.
Retail sales surge led to multilevel channel sales in which OEM lost the visibility of the end consumer sales as well as inventory at various levels. This led to dealer management systems (DMS) being developed to manage the channel sales. With advent of technology, DMS system was integrated with ERP. DMS evolved into a system to capture and manage downstream channel sales process with input from the ERP system.
"DMS evolved as the system for downstream channel sales process"
In the present landscape of IT systems for end to end to sales process there are three systems are being used in a collaborative environment.
The "Order to Cash" process
SAP S/4HANA has a very comprehensive OTC (order to cash) cycle, which is tightly integrated with manufacturing, procurement and finance and is a well-known system for processing customer orders.
Sales orders trigger the follow-on SAP supply chain activities like procurement and/or manufacturing if the stock is not already available as per the buyer’s requirements. For the selling cycle to be complete, the quantity required by the buyer must be delivered and the invoice must be sent to the customer. Finally, customers have to pay the money against the invoice. This whole process of creation of sales orders and receiving money from the customers is termed as the “Order to Cash” process:
Sales Order:
- Available to promise (ATP) - System will check the availability of stock in reference to the order quantity and the customer requested data and will propose the earliest delivery date possible.
- Pricing- Will be copied from the master data.
- Credit check – Check to ensure customer has not exceeded the credit limit.
Delivery processing
Confirmed sales order then have to be delivered to the customer. In SAP/4HANA, there are multiple steps which must be performed to ensure that the right SKU (the sales order with the required packing) is sent to the customer.
Steps in delivery processing:
- Pick – Identify the SKU in the warehouse and move it out of the storage rack
- Pack – Pack the SKU as per specifications lay out.
- Shipment – Load the SKU to the transportation vehicle (Road, Train, Air)
- Goods issue- Physically move the SKU out of warehouse and relieve the stock from the books of account
Invoice
Invoicing is the final step in the sales and distribution module of S/4HANA. Billing is created in S/4HANA either with reference to a delivery document or a sales order. When services are sold, there will be no material quantity involved, hence no requirement of a delivery document.
There are two steps in billing document: create the billing document in which price and other details are copied from preceding document, and release the billing document to accounting where the accounts receivable line and the revenue determination is created.
Order to Cash process course
Interested to learn more about the order the above information? Enroll in our our S/4HANA Order to Cash Course to learn about the logistics from beginning to end. The course will cover creating Master Data, using that data in the creation of the Sales Order, Delivery, Pick, Pack, and Goods Issues.
As a new SAP student, you will understand how to run the complete OTC cycle in S/4HANA. As an SAP Professional with knowledge of ECC 6.0, you will get an insight into the changes/enhancements in S/4HANA.
The following topics are covered in this Order to Cash process course:
- Sales planning
- Channel sales
- Master data for OTC
- Sales order
- Delivery
- Invoice
- Utilities in OTC
Have any questions? You can always reach out to the Michael Management Team for help.
Disclaimer: All images used are from Pramod Bangalore's MMC Courses
by Pramod Bangalore
Related Blogs

What's Broken about Budgeting?
How many people in your organization love the annual budgeting pro...

What is the Plan-Buy-Pay Process?
What is the Plan-Buy-Pay Process? The Plan-Buy-Pay process, which i...

Why are Companies Electing to use SAP EWM for...
In this article, my aim is to answer several questions about SAP EWM (Extended...
.png)